Sunlight contains ultraviolet radiation: ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) acts on the epidermis of the skin and causes erythema (reddening). When ultraviolet radiation interacts with 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin, vitamin D is produced. Things that can affect this conversion in the skin are – increased age, darker skin colour, the area of skin surface exposed and low levels of ultraviolet radiation (cloud cover/time of year). Although sun exposure can help increase vitamin D production, ultraviolet radiation is a risk factor for skin cancer and sun protection should be considered, especially in summer.
Minimal Erythemal Dose
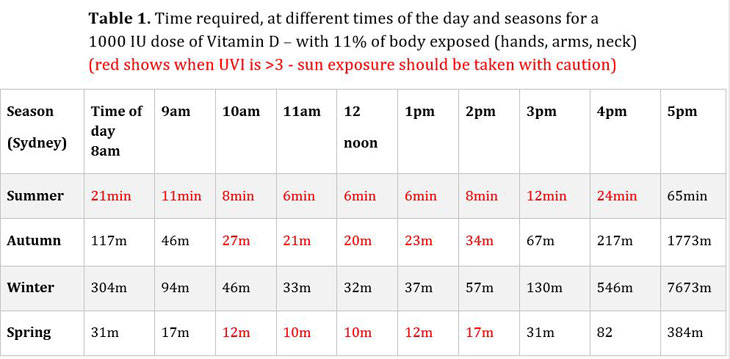
Or how much sun do I need? UVB penetrates the outer layers of skin, causing temporary redness (erythema). (It is the ultraviolet radiation A (UVA) that penetrates deeper layers of the skin, causing photo-ageing and increased risk of cutaneous malignant melanoma). The minimal erythemal dose (MED) is the minimum amount of exposure to ultraviolet radiation that causes erythema (reddening) of the skin. A MED required to synthesise 1000 IU of Vitamin D would depend upon the duration of sunlight which varies by time of day, season and city. The assumption that ¼ of 1 MED directed at ¼ of the body surface area (i.e., the face, neck, hands and full arms) allows for the equivalent production of 1000 IU of oral Vitamin D. For fair-skinned people, a dose of 1000 IU of Vitamin D would be achieved by exposing 11% of the body equivalent to 0.455 MED. If 17% of the body (hands, arms, neck and lower legs) were exposed that would equal a MED of 0.294. That is the more skin exposed the less time in the sun is needed to acquire a therapeutic dose of Vitamin D. Table 1. The time required, at different times of the day and seasons for a 1000IU dose of Vitamin D – with 11% of the body exposed (hands, arms, neck) (boxes in red indicate times the Ultraviolet Index (UVI) is >3 – when sun exposure should be taken with caution)








0 Comments